For preterm infants, the first emergency they face is not what many might expect. It’s not solely about breathing or warmth, but rather, it’s about nutrition. The importance of nutrition in the immediate postnatal period cannot be overstated, as it lays the foundation for a preterm infant’s growth and development.
Preterm babies, especially those born extremely preterm, are at a significant disadvantage when it comes to nutrition. Their early arrival into the world means their bodies are underdeveloped and not fully prepared to process nutrients.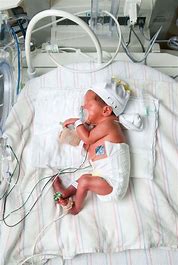
This is compounded by the fact that they have higher nutritional needs than full-term babies to support their rapid growth and development. Breast milk is widely recognized as the best source of nutrition for infants, including those born preterm. It provides a complex and dynamic fluid rich in nutrients, growth factors, and immunological components that are essential for the development of the neonatal gut and immune system.
However, the nutritional needs of preterm infants are so high that even breast milk alone may not be enough. And this is where human milk fortifiers come into play.
Human milk fortifiers are supplements added to breast milk to provide the additional nutrients that preterm infants require. They are specifically designed to provide the right balance of protein, minerals, and vitamins to support optimal growth and development.
Advanced human milk fortifiers such as NiQu HMoF not only provide the right quantity of proteins, vitamins and minerals but also bioactive factors such as HMOs (Human Milk Oligosaccharides), Lactoferrin, DHA and ARA. https://lnkd.in/gQYZyFqN
Evidence Backing Human Milk Fortifiers have shown that using them can improve growth outcomes in preterm infants. For instance, a randomized trial indicated that early human milk fortification increases length gain velocity and reduces declines in head circumference from birth to term equivalent age among infants born extremely preterm. Another study by the European Milk Bank Association highlighted the necessity of fortifying human milk with nutrients like protein, calcium, and phosphate to meet the high requirements of very low birth weight infants.
In conclusion, nutrition is indeed the first emergency a preterm baby faces, and human milk, when fortified appropriately, can meet this challenge. It’s crucial for healthcare providers to understand the unique needs of preterm infants and to use evidence-based practices, such as the early introduction of human milk fortifiers, to ensure these vulnerable babies get the best start in life.













